In numerical linear algebra, the Gauss-Seidel method, also known as the Liebmann method or the method of successive displacement, is an iterative method used to solve a system of linear equations. It is named after the German mathematicians’ Carl Friedrich Gauss and Philipp Ludwig von Seidel and is similar to the Jacobi method. Though it can be applied to any matrix with non-zero elements on the diagonals, convergence is only guaranteed if the matrix is either strictly diagonally dominant, or symmetric and positive definite.
Gauss-Seidel Method Solved Example
Solving systems of linear equations using
Gauss-Seidel method.
2x-3y+20z=25
20x+y-2z=17
3x+20y-z=-18
Solution:


C Program
//Gauss Seidel
//This code is written by Souvik Ghosh
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <math.h>
//diagonally dominant form
#define f1(x,y,z) (17-y+2*z)/20
#define f2(x,y,z) (-18-3*x+z)/20
#define f3(x,y,z) (25-2*x+3*y)/20
void main(){
float x0=0,y0=0,z0=0,x1,y1,z1,e,e1,e2,e3;
printf("enter the tolerable error\n");
scanf("%f",&e);
int count =1;
printf("Iteration\tx1\ty1\tz1\n");
do{
x1=f1(x0,y0,z0);
y1=f2(x1,y0,z0);
z1=f3(x1,y1,z1);
printf("%d\t%0.4f\t%0.4f\t%0.4f\n",count,x1,y1,z1);
//error
e1=fabs(x1-x0);
e2=fabs(y1-y0);
e3=fabs(z1-z0);
count++;
//set the value for next iteration
x0=x1;
y0=y1;
z0=z1;
}while(e1>e&&e2>e&&e3>e);
printf("\nx=%0.4f\ny=%0.4f\nz=%0.4f\n",x1,y1,z1);
}
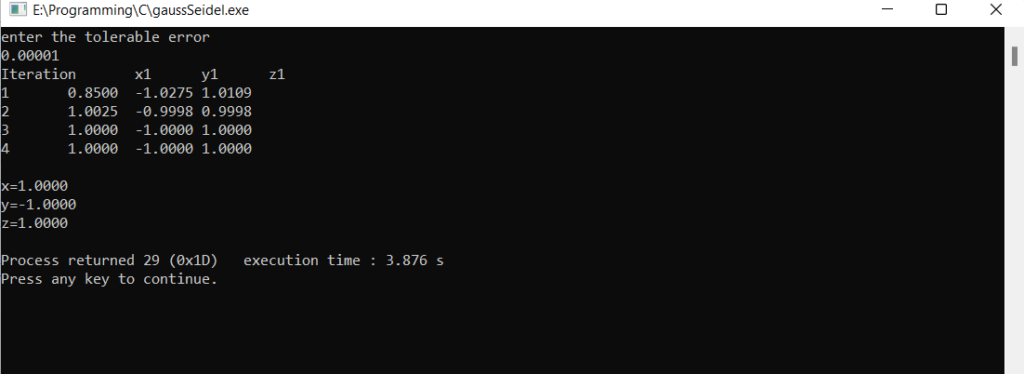
Output Terminal